Differences Between Handheld Computers and Handheld Code Readers
Just like handheld computers, handheld code readers are another type of device that is commonly used to read a variety of data. Both of these are handheld devices that operators use to read barcodes and similar information, but the similarities end there. The additional functions and applications of these devices are different. This section investigates the differences between handheld computers and handheld code readers by comparing their functions and specifications.
Specifically Designed, Simple-function Handheld Code Readers and Highly Applicable, Multi-function Handheld Computers
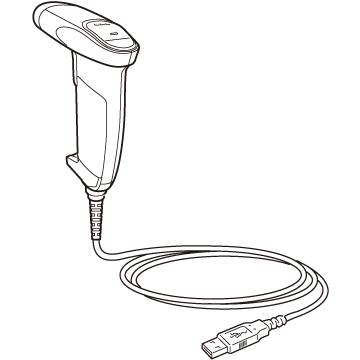
Handheld code readers are one type of barcode readers and are simple-function products specialized just for reading codes. The read data is processed by the connected PC or similar device, so there is no program within the handheld code reader. These devices do not function unless they are connected to a PC, so they are not suited for usage in which they are separated from a PC and carried around like a handheld computer.
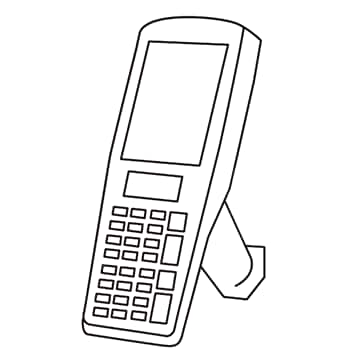
On the other hand, a handheld computer has an embedded program that enables it to not only read data but also to perform other required processing such as checking (displaying) and saving the read data. This program can be rewritten to match the application and purpose.
Furthermore, there are batch type handheld computers that accumulate data internally before processing it and wireless type handheld computers that send and receive data on demand. One of the features of handheld computers is that, basically, they can function in a standalone manner. This is a major difference with handheld code readers, which do not function unless connected to a PC or a similar device.
Handheld code readers are handheld barcode readers. Handheld computers are multi-function, mobile terminals designed to perform operations such as displaying, checking, saving, and sending the read data. Another major difference between the two is handheld computers can function in a standalone manner, without a PC. A detailed function comparison is shown below.
| Comparison item | Handheld computer | Handheld code reader |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance |
 |
 |
| Functions |
|
|
| Operating range |
|
|
| Program |
|
|
| Others |
|
|
| Common usage examples |
|
|
| Conclusion |
By changing the program, a handheld computer can be used in a variety of applications. |
Handheld code readers are simple-function devices designed just to read codes. They can be installed with simple connections and at a low cost, but the situations in which they can be used are limited. |